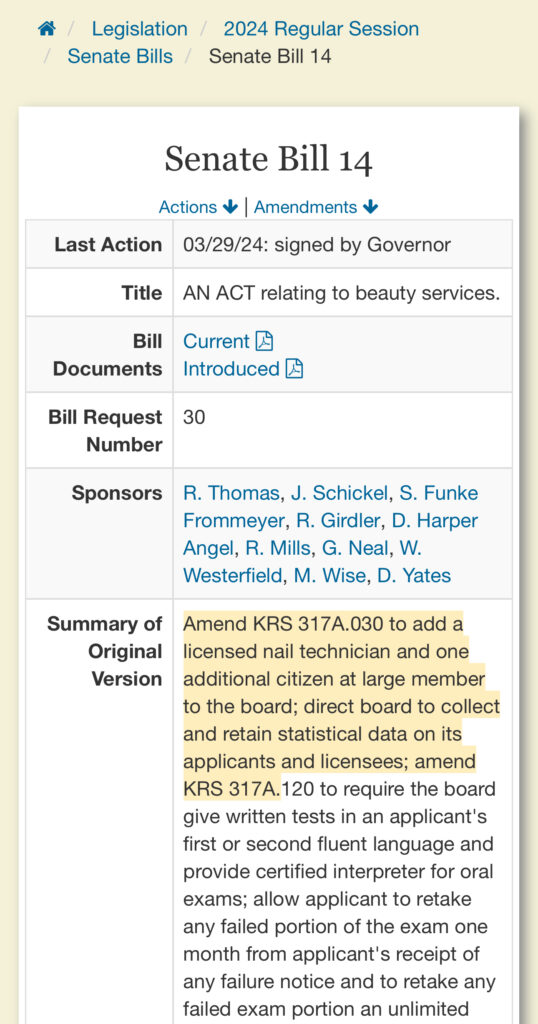
On March 29, 2024, Governor Andy Beshear signed Senate Bill 14 into law, marking a significant advancement in the beauty industry’s efforts toward diversity, inclusion, and workforce development. Sponsored by Senator Reginald Thomas and a bipartisan group of legislators, the bill amends several key statutes to make the cosmetology and nail technician professions more accessible and equitable, particularly for immigrants and underrepresented populations.
Key Provisions of Senate Bill 14
The bill introduces several important changes aimed at creating a more inclusive environment for beauty service professionals:
1. Expanded Board Representation: The Kentucky Board of Cosmetology will now include a licensed nail technician and an additional citizen-at-large member, ensuring that the board reflects the diversity of the industry it regulates.
2. Language Accessibility: Written tests for licensing will be available in an applicant’s first or second fluent language, and certified interpreters will be provided for oral exams. This measure is crucial for non-English speaking applicants, many of whom are immigrants seeking to establish their careers in the United States.
3. Retesting Flexibility: Applicants who fail any portion of the licensing exam can retake the failed portion one month after receiving a failure notice, with no limit on the number of times they can retake the exam. The retesting fee is capped at $35 per exam, reducing financial barriers for aspiring professionals.
4. Violation Remediation: The bill requires that a warning notice be issued for violations, except in cases that present an immediate and present danger. This approach allows salon owners and technicians to correct issues without facing immediate penalties, fostering a cooperative relationship between the industry and regulators.Implications for Diversity and Inclusion
Senate Bill 14 is a testament to Kentucky’s commitment to diversity and inclusion within its workforce. By removing language and financial barriers, the bill opens up opportunities for individuals from diverse backgrounds to enter and thrive in the beauty industry. This is particularly significant for immigrants and underrepresented groups, who often face challenges in obtaining professional licenses due to linguistic and economic obstacles.
Furthermore, the bill’s emphasis on fair treatment and remediation in case of violations promotes a more just and equitable regulatory environment. It acknowledges the importance of providing all industry participants with the opportunity to succeed and rectify mistakes, thereby building trust between the government and the beauty services sector.
In essence, Senate Bill 14 is not just a legislative change; it is a reflection of Kentucky’s dedication to creating an inclusive, diverse, and skilled workforce. By embracing the rich tapestry of cultures and languages that makeup its population, the state sets an example for others to follow in promoting diversity and inclusion in all professional fields. This law is a step forward in ensuring that the beauty industry, a sector that celebrates diversity and self-expression, is accessible and welcoming to all who wish to be a part of it.
https://apps.legislature.ky.gov/record/24rs/SB14.html